Upon arriving in Bigwin Island, some 160 miles north of Toronto on the Lake of Bays, it is simple to see why this peaceful and remote backdrop once lured celebrities, dignitaries, and tycoons. But long before the first golf course and resort opened here in 1922, it was a historic, sacred site for Indigenous peoples-in fact, the island is named for Ojibway Chief John Bigwin.
Today, the property is owned by Jack Wadsworth. He wanted to restore that sense of reverence for the land, and so he hatched the idea for a community of cabins planted in the midst of Bigwin Island’s maple, pine, and ash tree forests. With the help of Halifax, Nova Scotia-based MacKay-Lyons Sweetapple Architects, his vision is slowly coming to life.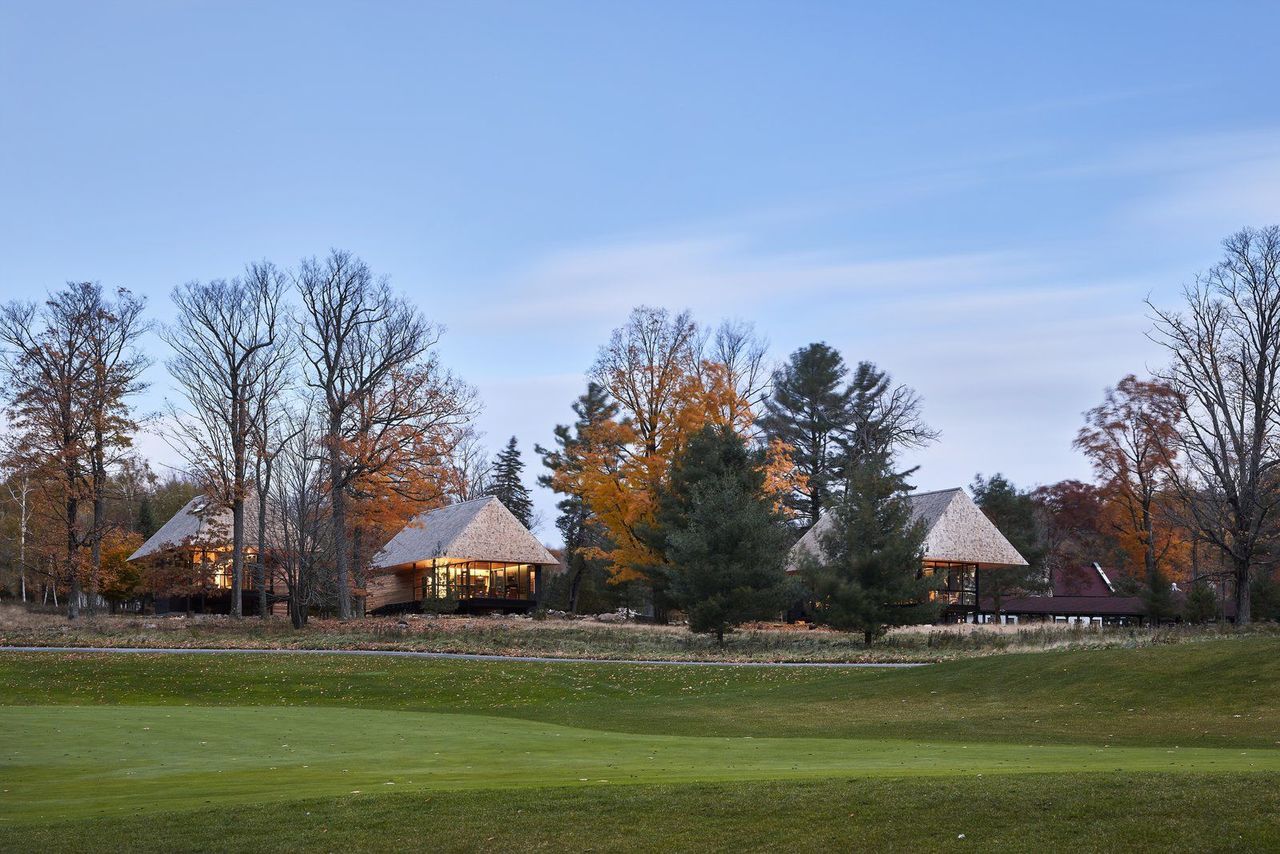 
The cabins, in close proximity to one another, are to designed to spark chats between neighbors.
Unhappy with the idea of a hotel sprouting on the site, Wadsworth instead decided that a complex of 40 guesthouses, between 1,230 and 1,350 square feet, would better respect the surroundings and espouse a carefree holiday feel. When he invited six different Canadian architecture firms to present proposals, Wadsworth asked that they prioritize sustainability in their designs, while being considerate of the environment and the Muskoka region’s architectural heritage. The chosen plan from MacKay-Lyons Sweetapple Architects does exactly that.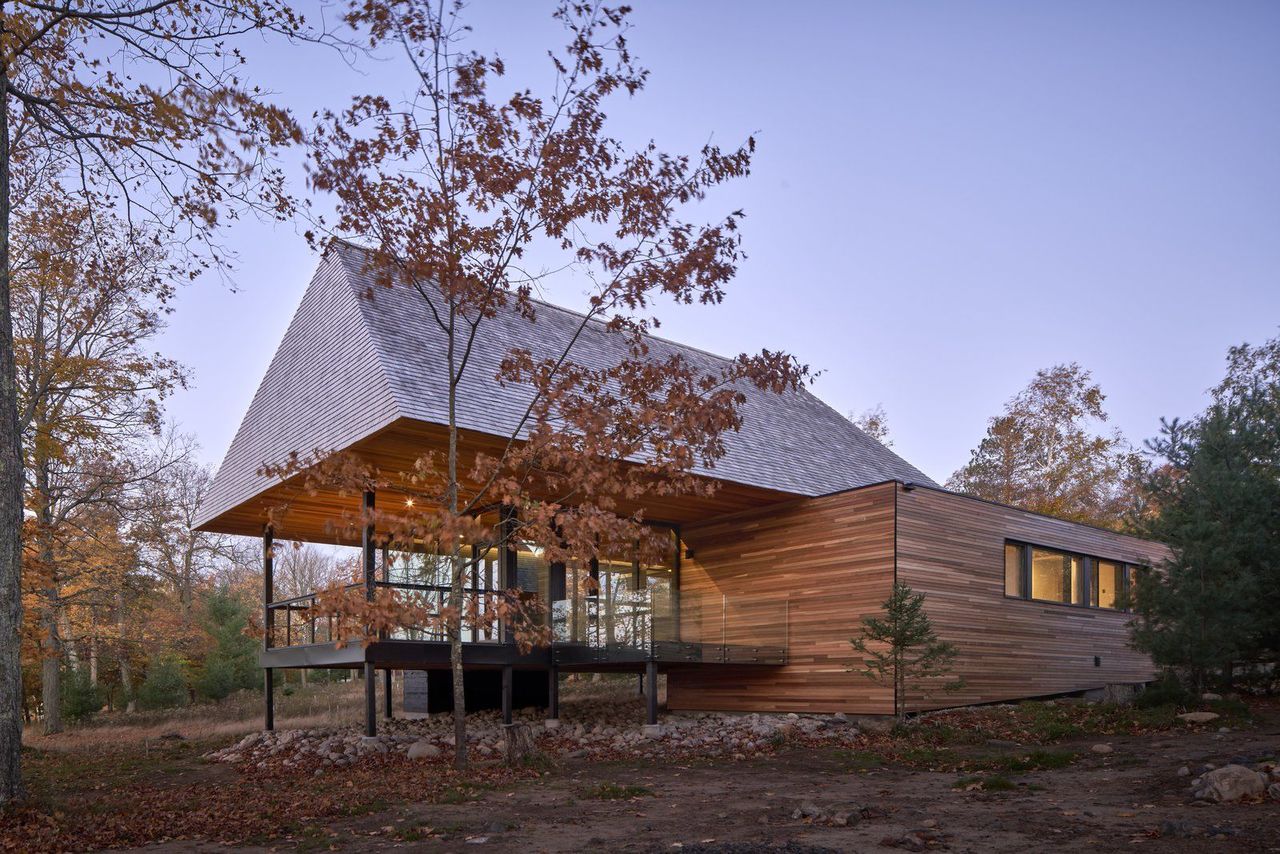 
The glass pavilion rises into a peaked roof, one of the cabin's most distinguishing features.
"John’s family had been coming to Bigwin Island for decades. He really cares about the place," says partner Brian MacKay-Lyons, who ensured that there was little disruption to the terrain. In fact, he describes the Bigwin Island Cabins as "a simulation of how architecture without architects happens."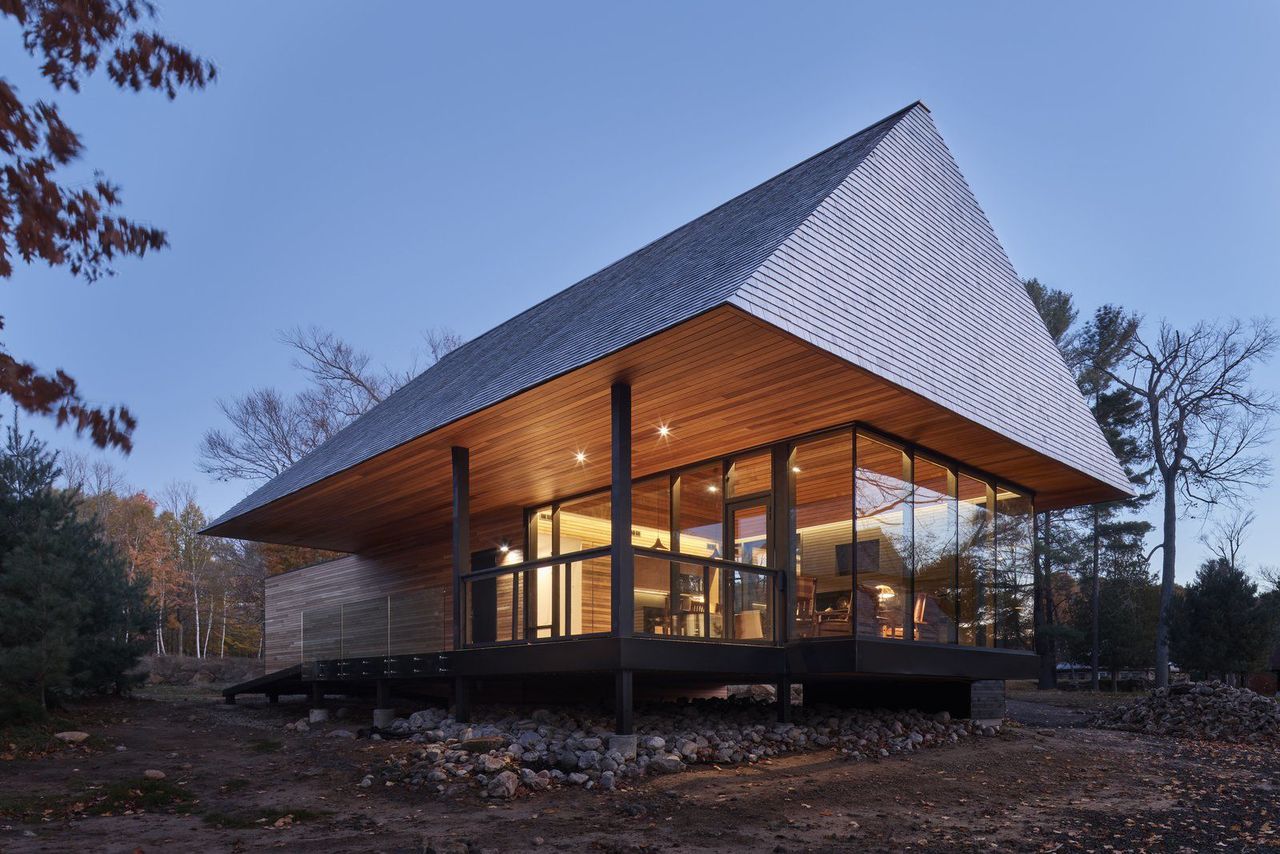 
In the winter, a geothermal heating system harvests heat from the lake and radiates it from the floors. Come summer, a natural, passive ventilation system is in place, sending hot air up and out through the roof.
Deer, thanks to their unpredictable grazing habits, organically created site lines to the lake and golf course; MacKay-Lyons merely responded. "The deer on the island are the architects. The soffits the big roofs float on, that's really the grazing line made by the deer. There are no bad views," he explains.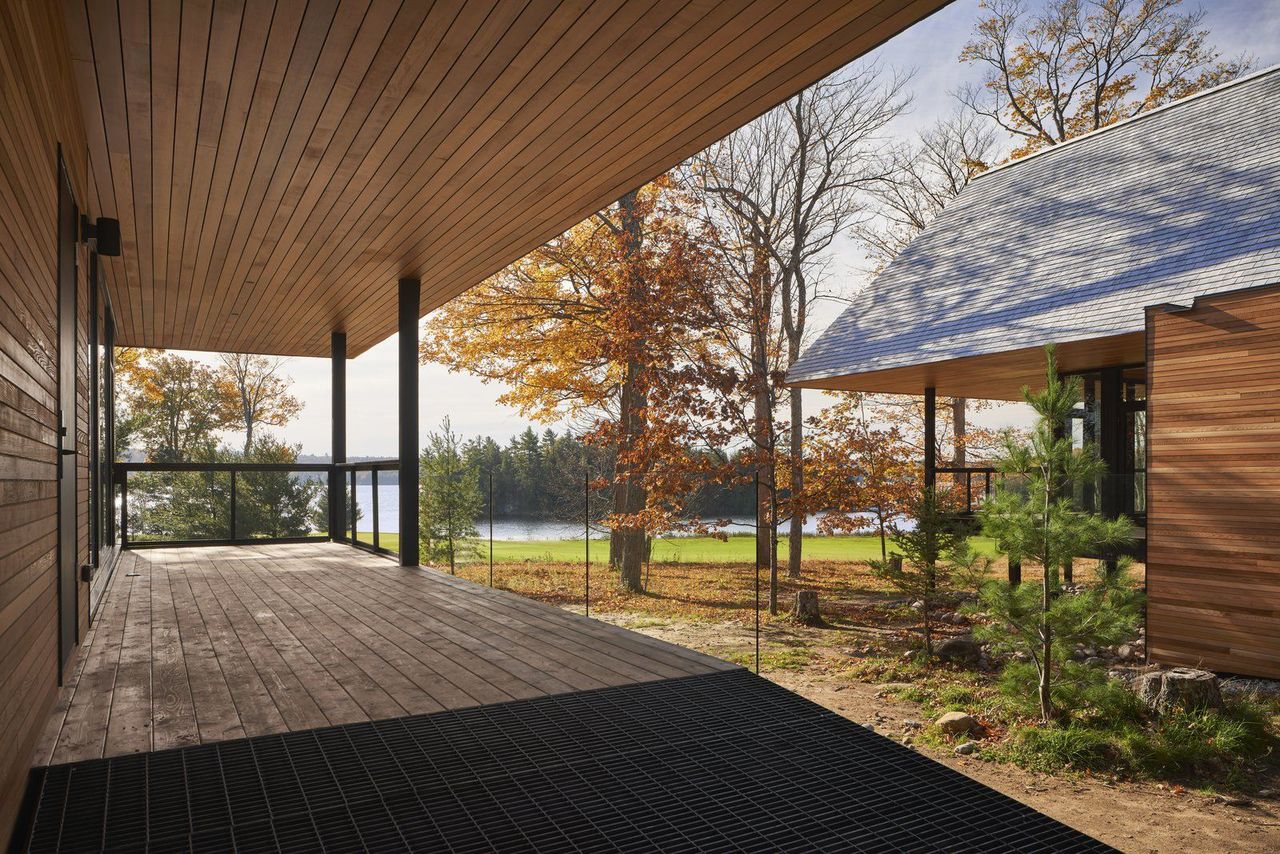
The linear cabin flaunts a rectangular shape.
So far, MacKay-Lyons has completed three different versions of the cabins, all of which are spawned from local materials and capped in enormous roofs that nod to cottages and boathouses found throughout Muskoka.
"Whenever I look at a region, I look for a prototype," he points out, noting that these roofs are not just familiar references, but imbue each cabin with a feeling of protection through "these single sheltering pyramids."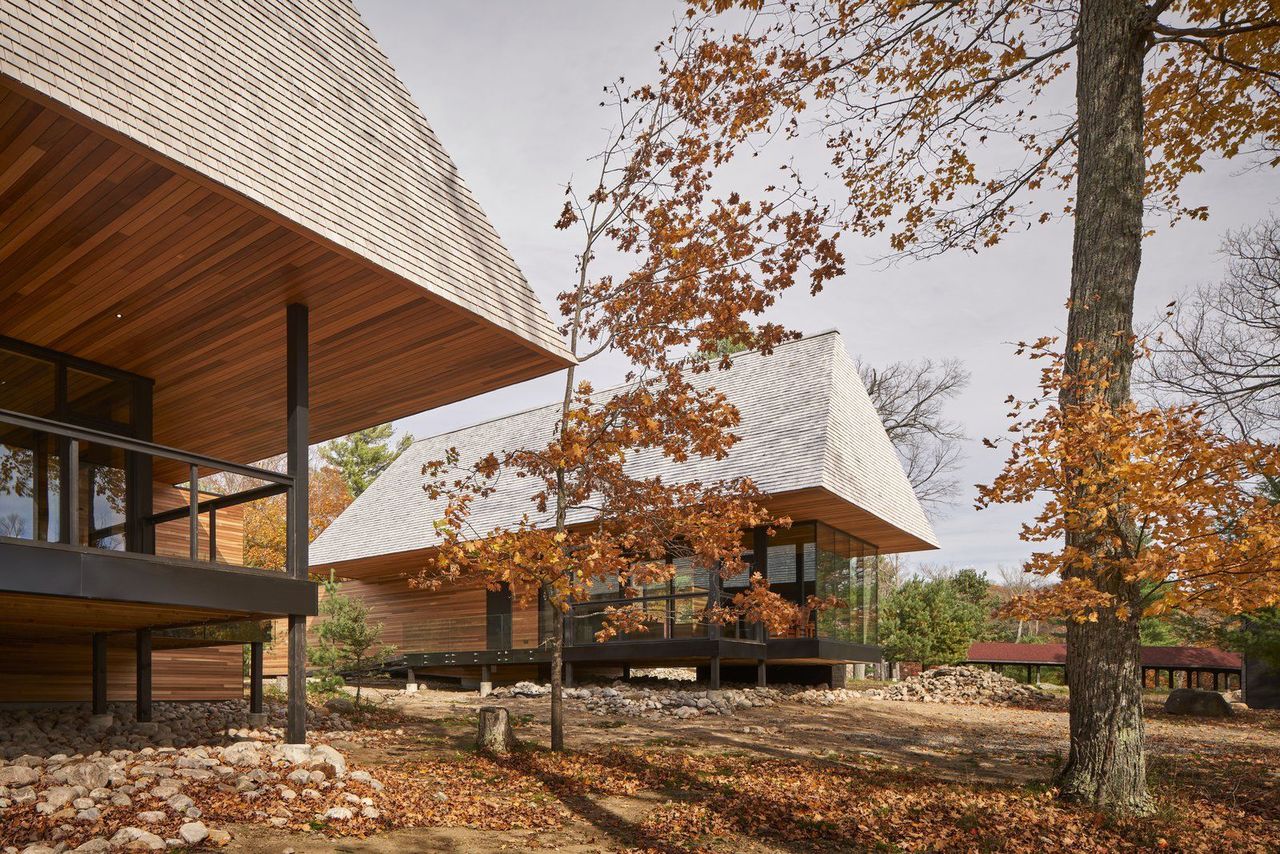 
Those massive cedar shingle roofs add a sense of comfort and protection to each cabin.
One style of cabin is linear; those in the woods embrace a courtyard layout; and the ones on the meadow are pinwheel shaped. All three simple forms are assembled from the same blocks: a screened-in porch, a deck, a hearth, a great room, a sleeping box, and a hip roof covered in cedar shingles.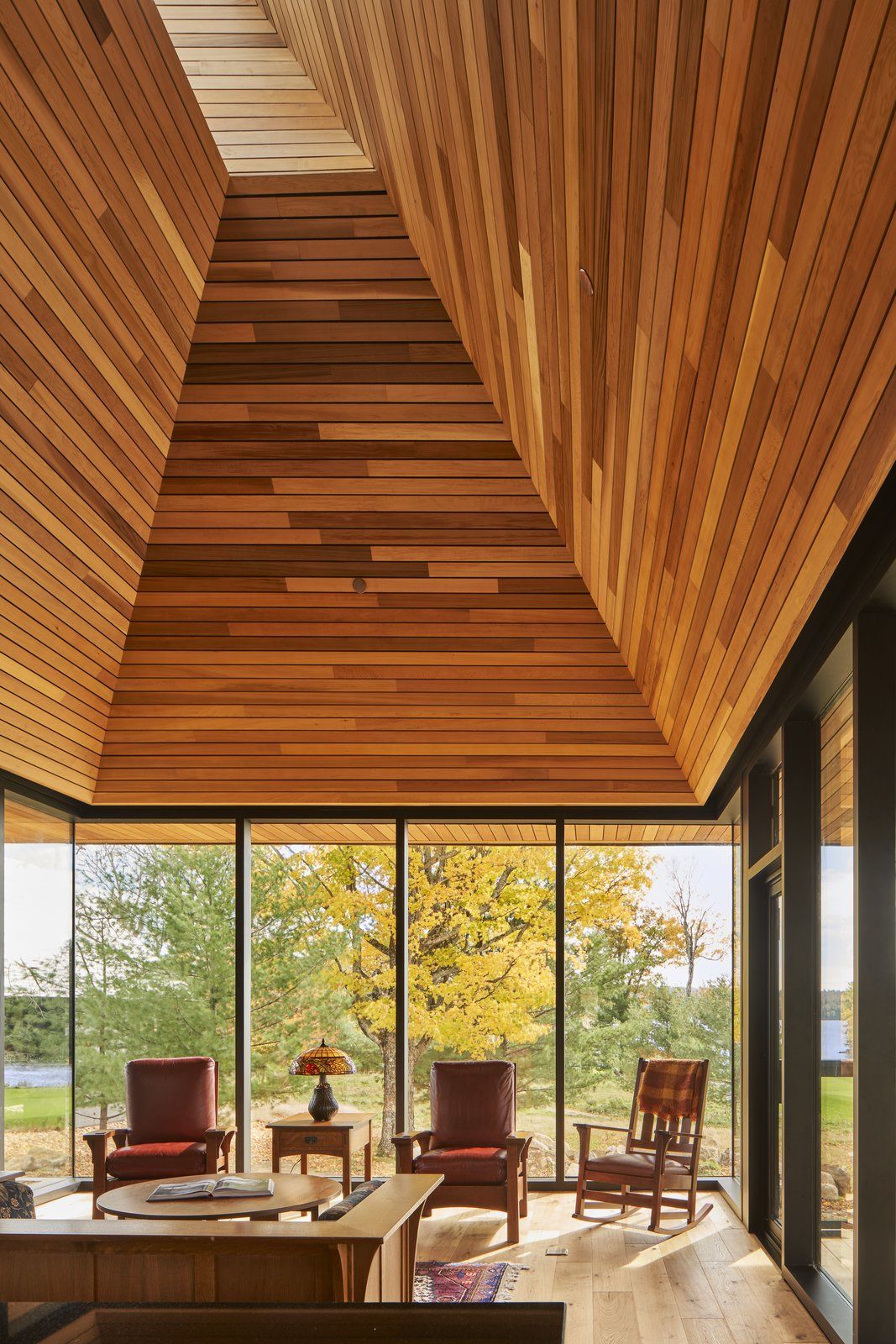 
As this view of the lake confirms, the landscape is powerfully visible from all cabins.
A glass pavilion containing the open-plan living and dining areas soars to a peak and seamlessly connects to the rest of the cabin, an extruded box that is clad in rustic shiplapped wood. Inside, there is more of the same earthy materials, subtly suggesting a canoe and creating continuity between the indoors and outdoors, amplified by natural light coming in from a skylight above.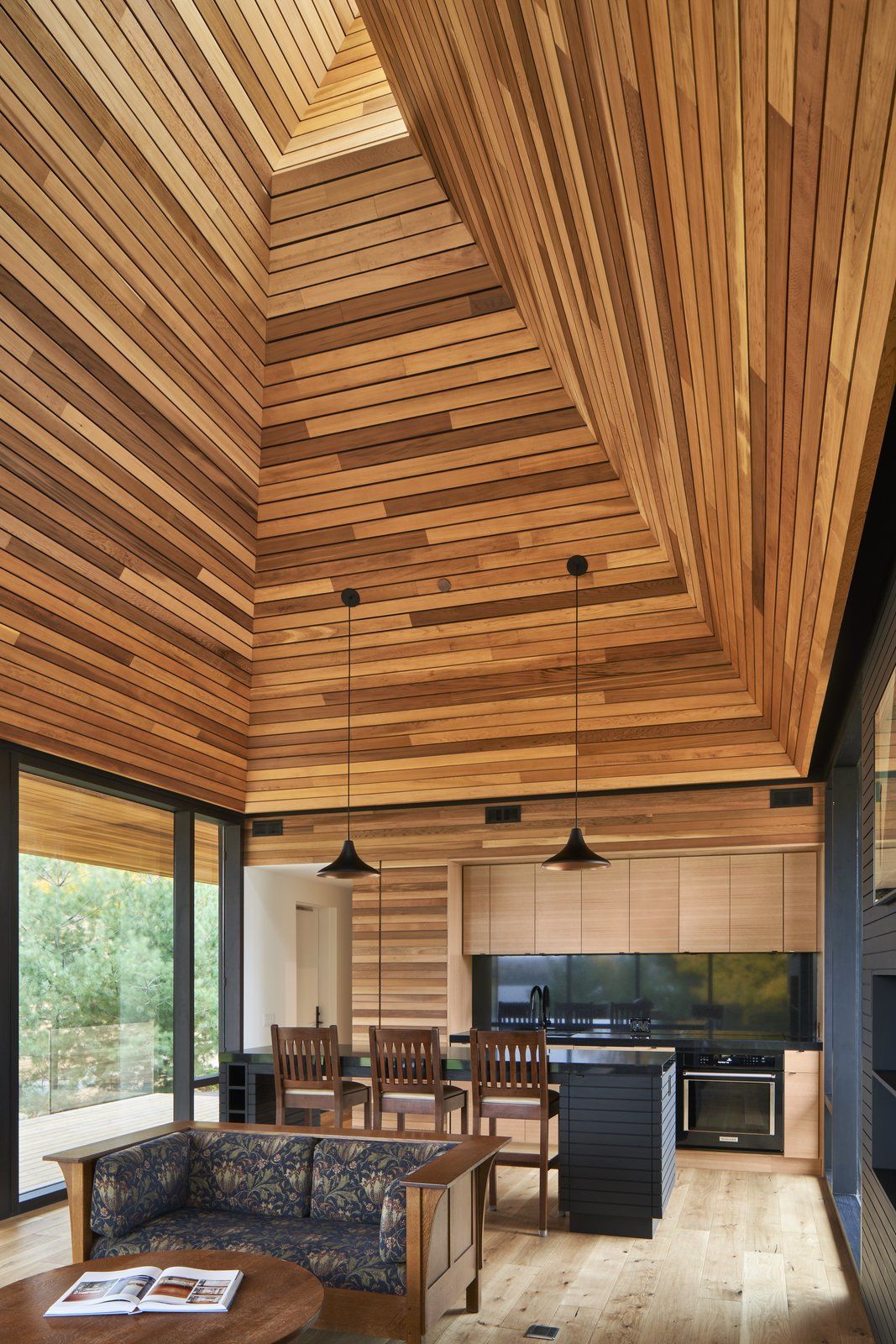 
The living and dining areas flow into one airy space.
Since the landscape is the focal point of the Bigwin Island Cabins, each unit is designed to maximize its immediate setting and the vistas beyond, yet reveling is not meant to be a solo ritual in this budding community.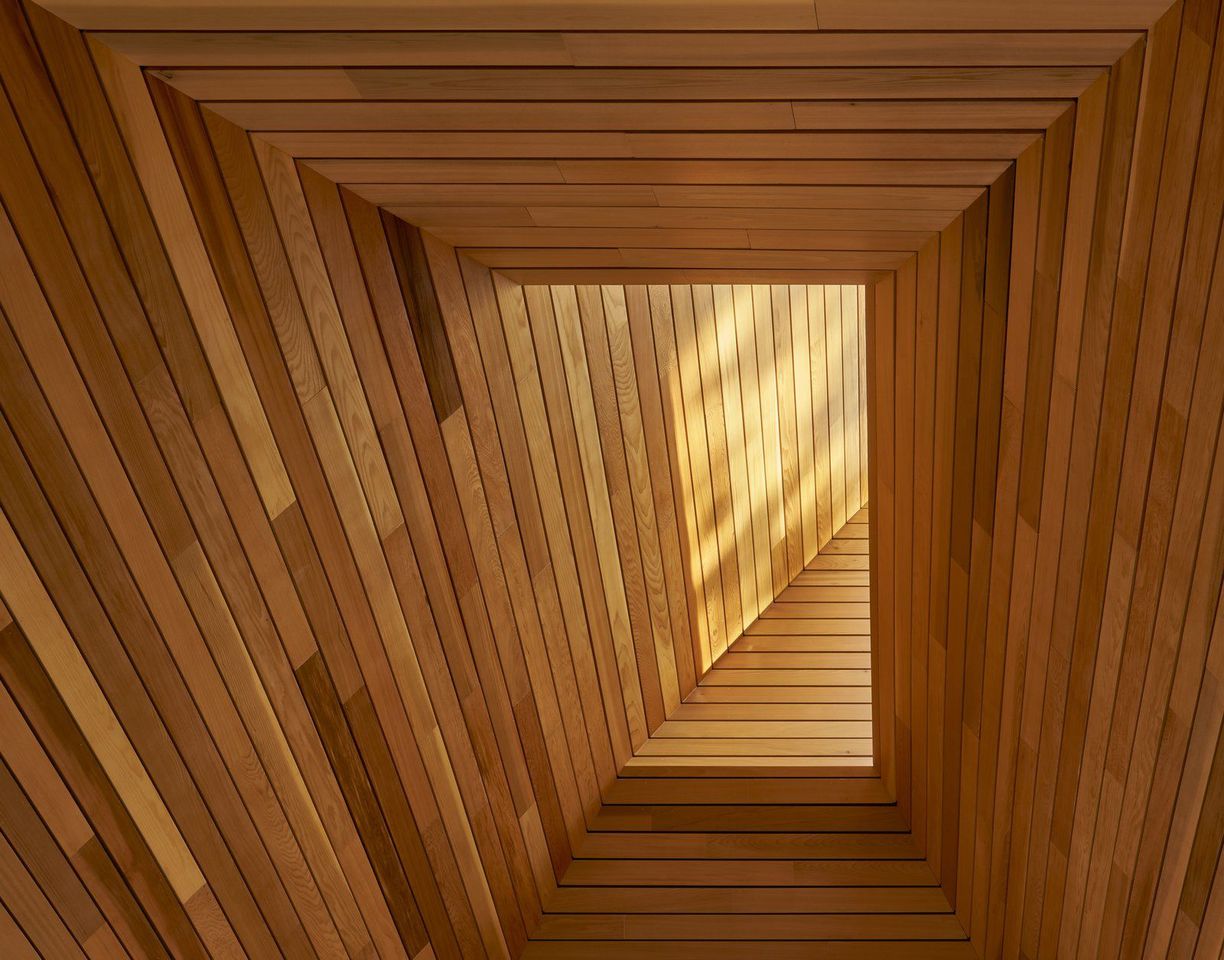
A close-up of the ceiling, which is punctured with a skylight.
These transparent cabins are arranged in clusters to invite spontaneous, old-fashioned conversations with neighbors. "We developed a grammatical system for how these elements can combine in various ways to make a house, and also how the houses can aggregate to make a village," says MacKay-Lyons.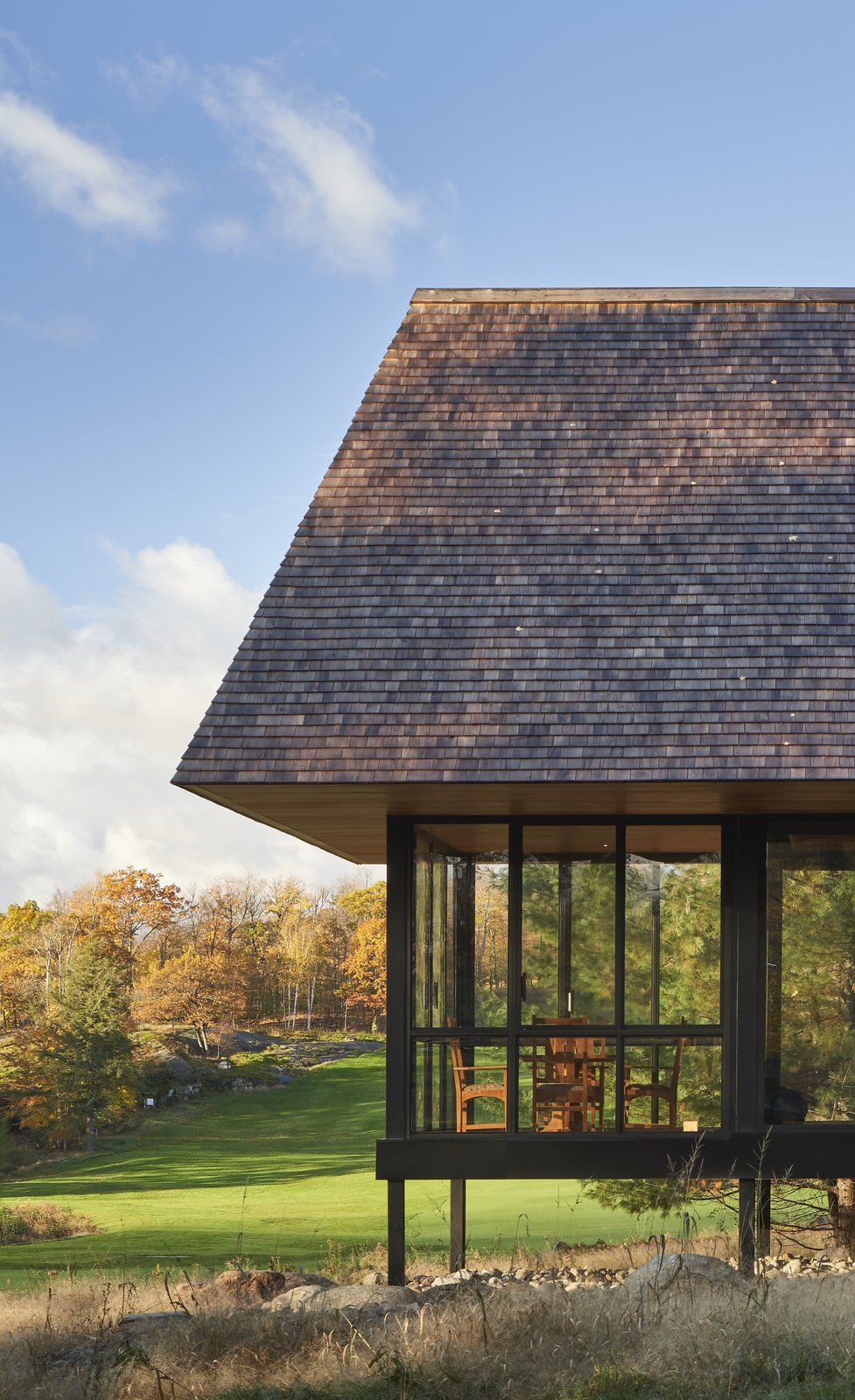
The dining area, situated in the open glass pavilion, essentially translates to "eating alfresco."
Thirty-seven cabins are currently under development, and MacKay-Lyons is okay with the slow progress, as that process breeds dynamism: "Time is your friend. It allows for a feedback loop. What will happen is these will vary quite a bit as we learn more about how to optimize them. Communities completed all at once tend to be stillborn." 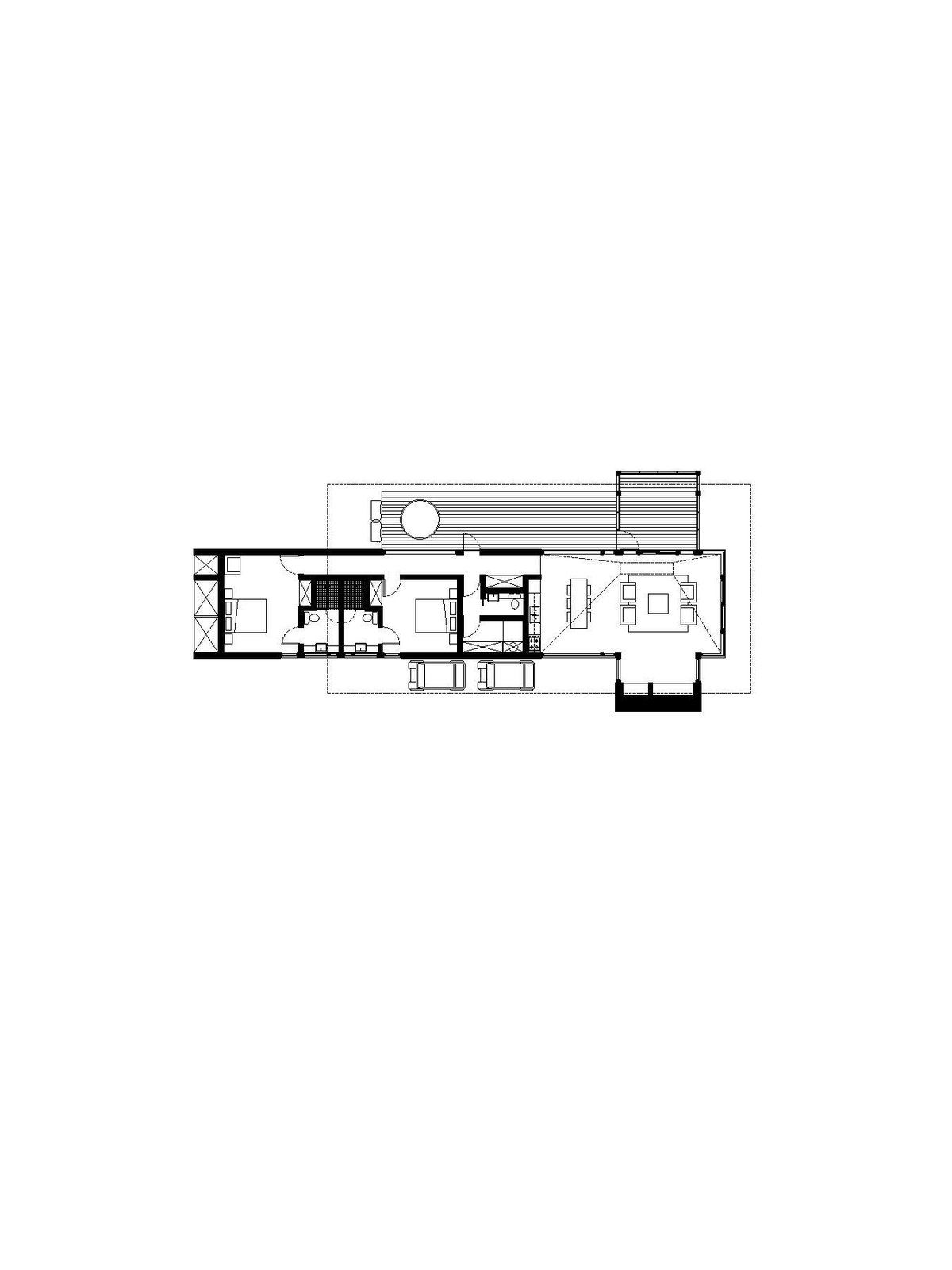
Floor plan for the linear cabin.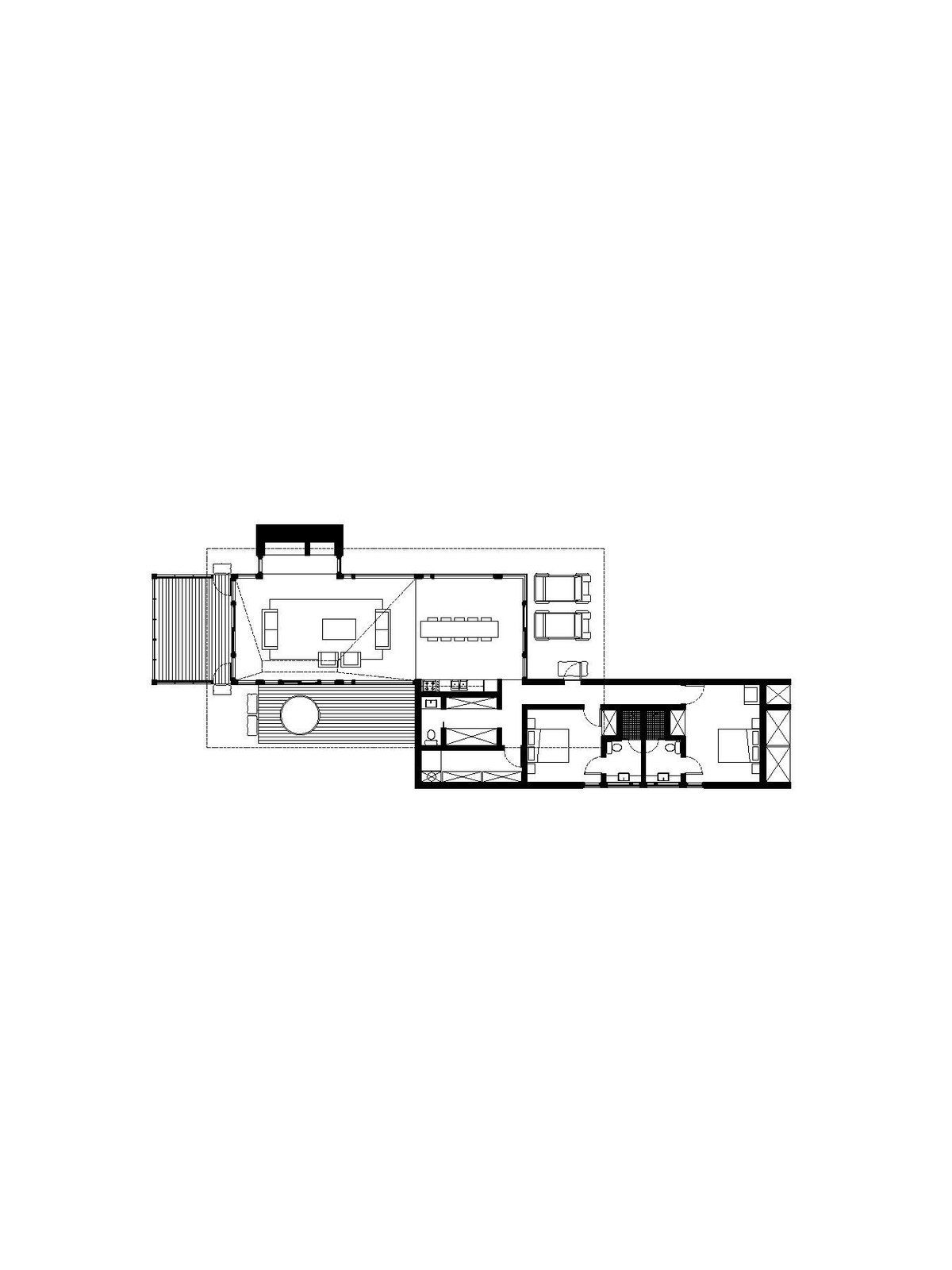
Floor plan for the pinwheel cabin.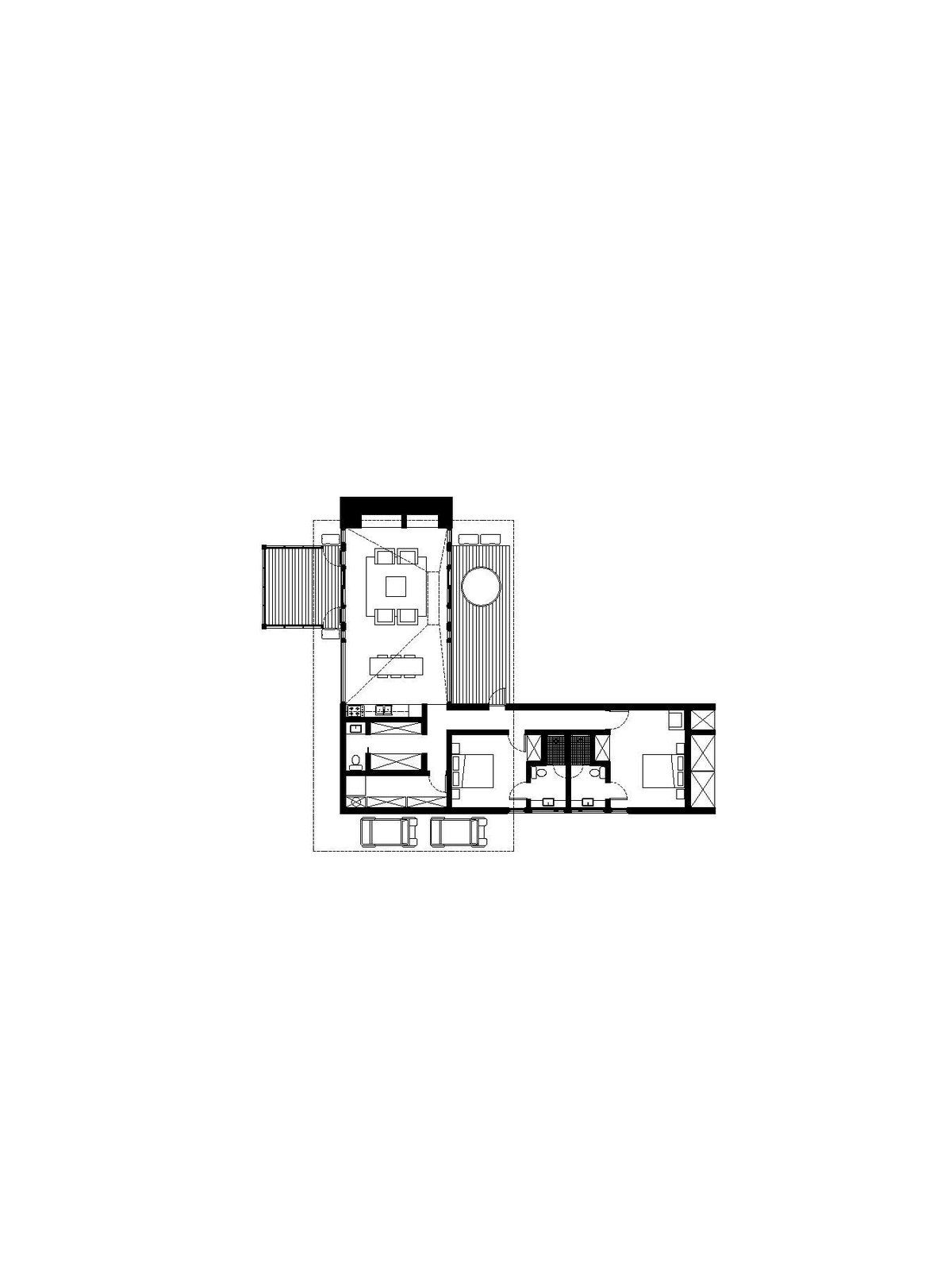
Floor plan for the courtyard cabin.

Tropical Boho Homes With Beautiful Vignettes & Vistas
Two tropical boho home designs, featuring swimming pools, cozy lighting schemes, interior archways, natural accents, and beautiful decor vignettes.


![A Tranquil Jungle House That Incorporates Japanese Ethos [Video]](https://asean2.ainewslabs.com/images/22/08/b-2ennetkmmnn_t.jpg)









